
By Muktirajsinhji Chauhan, School of Architecture at Ahmedabad
Adherence to Vastu Shastra, the ancient and medieval canons on city planning and architecture, has suddenly assumed tremendous significance, particularly among the well-educated and affluent in urban India. It may be difficult to predict if this is just a fad or if it will be a way of building dwellings, offices, and factories etc. for many years to come.
Interestingly, practically none of the practitioners of Vastu Shastra has an academic background. So there is a lot of genuine practice as well as hearsay going around. In this brief introduction, the intention is to give a broad overall picture of the Vastu Shastra with some examples.
Vastu Shastras are canons dealing with the subject of vastu which means the environment. Put differently, one may regard them as codification of good practices of design of buildings and cities, which will provide settings for the conduct of human life in harmony with physical as well as metaphysical forces. These Vastu Shastra canons provide guidelines for design of buildings and planning of cities such that they will bring health, wealth and peace to the inhabitants.
 Mythological beliefs are certainty at the root of the origins of these canonical texts and their discourse. The first of these relates to Vastupurusha, which appears to be the first step in ordering a part of the vast cosmic space, the brahmanda, for human habitation. According to myth, long ago there existed an unnamed, unknown and formless being which blocked the sky and the earth. The Gods forced it down on earth and pressed it face down. To ensure that it did not escape again, Lord Brahma, the supreme creator, along with other gods weighted it down and called it vastupurusha.
Mythological beliefs are certainty at the root of the origins of these canonical texts and their discourse. The first of these relates to Vastupurusha, which appears to be the first step in ordering a part of the vast cosmic space, the brahmanda, for human habitation. According to myth, long ago there existed an unnamed, unknown and formless being which blocked the sky and the earth. The Gods forced it down on earth and pressed it face down. To ensure that it did not escape again, Lord Brahma, the supreme creator, along with other gods weighted it down and called it vastupurusha.
Lord Brahma, of course, occupied the central portion and in a hierarchic distribution along concentric rings assigned different quarters to different major and minor gods. Thus emerged a geometric configuration, which is called mandala. From one basic square, the canons have listed up to 1024 divisions of a square and given each one a name. The most popular among those have 64 and 81 divisions known as Manduka Mandala and Param Sayika Mandala, respectively, which are widely used for temple and dwelling plans.
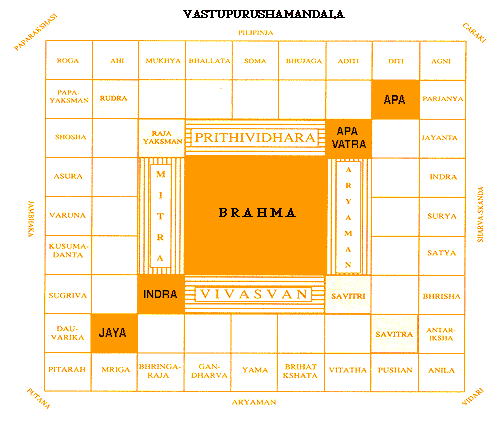
The mandala is also given an orientation with Surya, the sun-god, occupying the central point of periphery to east; Varuna, the Lord of winds, to the west; Kubera, the Lord of Wealth, to the north; and Yama, the Lord of Death, to the south. The rest of the squares are occupied by the other minor gods. With the positions thus assigned and the beneficial or otherwise attributes of gods established through other myths, it is possible to assign the activities of living, working and support facilities over the mandala and therefore the layout of a city or a building.
The mandala is, of course, the most popular aspect of the vastushastras as it is constantly referred to for the location of the various activities in a building. The proper texts themselves, however, deal with a wide range of topics relating to built-environment. These include site selection, soil testing, building materials and techniques, design of temples separately by number of floors, palaces, dwellings, gates, image of the deity, their vehicles and seats even including the making of image of a linga for Shiva temples. All these are treated in different chapters of the canonical texts.
As an example, one may mention the matter of site selection, which is dealt with in both scientific and religious terms. The method of digging a pit and refilling it with excavated earth is given scientific treatment. If a lot of earth is left out, then the soil is compact with good load-bearing capacity.
A similar test checks the seepage of water in the soil. It if is quick, the soil is obviously not good. The religious prescription suggest that if the soil is white with ghee-like smell, it is good for Brahmins, if red with blood-like smell it is good for Kashtriyas, yellow with smell like sesamum oil, it is good for Vaishyas and black with the smell of rotten fish, it is good for Shudras. While the first two suggestions would still find the approval of a modern engineer, the third more likely betrays the caste-ridden nature of some of the Shastra's recommendations.
The Shastras also deal at length with town planning and form of towns suitable for different purposes such as administrative towns, hill towns, coastal towns or religious towns built at a sacred place. Among the most famous examples of a town planned according to these standards is the example of Old Jaipur which is based on a Prastar type town described in several texts. Built in 1727 AD, the final form and structure of the town shows a skillful manipulation, according to the Shastra's prescriptions, of the square mandala right from the whole to the smallest of the plots, the location of activities, and distribution of the caste groups.

Jaipur City Palace
Based on the studies carried out by scholars it is suggested that these texts were written down largely between the 7th century AD to 13th century AD following the Gupta period. They are found in all the major languages of medieval India. Of course, the earliest references are also found in the Vedas, which deal with carpentry among other subjects.
Vastusastras can be said to be companion texts to Shilpasastras and Chitrasastras dealing with sculpture, icons and painting respectively. Strangely, among all these texts, those devoted exclusively to one of the areas. i.e. vastu, chitra or shilpa are rare. This is because in the Indian artistic traditions, each was an important and integral part of the creative endeavor largely because all of these, including performing arts such as the dance and music, were based at the temple.
Among the vasthusastra texts are Mansar, Maymata, Vishwakarma and Samrangana Sutradhara which is credited to Raja Bhoja. The others are believed to have been authored by ancient saints and sages. These include Lord Vishwakarma who is architect to the gods in the Nagara or northern traditions, and Maya who is architect to the gods in the Dravida or Southern tradition. In the northern tradition Maya is regarded as architect to the danavas or demons. To give some idea about the size of the text, Masar comprises 5400 verses organized in a total of 70 chapters. 
However, the nature, content and format of the texts as discussed above is in total contrast to the books that have recently been published and gone through, in some cases, half a dozen reprints in a span of one year. They share very little in common. As to what are the origins of the practitioners' texts recently published, I can only suggest that these would he more ritualistic practices broadly interpreted by the various puranic texts such as Agni Purana, Matsya Purana and their Agmic versions in the Dravidian traditions. The parallel I can draw upon is of Brigusamhita used by the palmists, which by itself has no serious pretensions to astronomy. The practitioners themselves are silent and unresponsive when questioned about these aspects.
One of the more recent texts goes so far as to suggest the location of two weighing scales in different parts of the plot in a factory. One was for weighing raw materials which would in that location weigh less than actual, and the other one of weighing finished goods which would register more weight than actual. Very neat, one may say, and very tempting for the factory owner.
 As to the beneficial aspects of following these suggestions, the available experience is equally divided. There seems to be an equal number of success stories as well as failures. Here, I believe, the analogy of the typical palmist is best. Perhaps there are genuine jyotish shastris as well as frauds. Is it that human beings want to be able to put blame on some unknown forces for failures? Or that they would want to appease the unknown to ensure a success? These are more a matter of faith rather than belief.
As to the beneficial aspects of following these suggestions, the available experience is equally divided. There seems to be an equal number of success stories as well as failures. Here, I believe, the analogy of the typical palmist is best. Perhaps there are genuine jyotish shastris as well as frauds. Is it that human beings want to be able to put blame on some unknown forces for failures? Or that they would want to appease the unknown to ensure a success? These are more a matter of faith rather than belief.
Fortunately, Indians are not alone in this in recent times. Across Asia there is a resurgence of these beliefs and practices. Feng-shui, the Chinese version of Vastusastras, is practiced all over the Far East and South-east Asia. There, too, the situation is one of either you believe and practice or you don't believe and don't practice. Does this mean that one cannot explain this on a rational basis?
These texts (i.e. the genuine ancient and medieval canons) dealt with the classical manner of arts and architecture. This meant that irrespective of who was doing what and where, a certain quality, content and perfection would always be achieved just by following the texts. To paraphrase Einstein's observation for a similar work, "it makes good easy and bad difficult". This means that a temple made on the banks of Ganga would be as perfect as one made on shipra though patronised and designed by different persons.
Even those uninitiated can learn and practice the entire range of connected activities right from the selection of a site to the execution of all the elemental details. Then there is some reason to believe that some of the suggestions may indeed reflect more real concerns such as climatic suitability of locating the human activities in a building. An entrance front north ensures that it will always be in cool shade in India, besides allowing the wealth to flow in as it is the direction of Lord Kubera. The next alternative of entrance from east certainly brightens up the morning environment with the first rays of sun to start a great new day on a cheerful note.

Then there is a metaphysical aspect to it all. This one concerns the fears of the unknown on one hand, and attempts to intellectually grasp the nature of the world on the other hand. And between these two is the human desire to do things right, in conformity and in harmony with the unknown world and its forces. This is where particularly the mandala diagrams become very useful. These, in abstract terms, manifest or represent the cosmological conception of the world, albeit the world as conceived or interpreted by the ancient and the medieval scholars.
It is therefore natural that buildings and cities which represent a significant alteration of the terrestrial world be based on the mandala to make them harmonize with the unknown world. In other words, it, is undertaking a human act in tune with the nature as well as the unknown in the belief that these will not clash but work harmoniously to bring peace and prosperity to the builder and the inhabitants.
Architecture is a human act. It requires carving out a segment of that omnipotent, universal space of the brahmanda, the cosmic space, for the use of the human beings. It is not often that architecture truly rises to the challenges of capturing the divine character of the brahmanda in its folds. When it does happen the architectural experience exalts generations of people to come. Is this not true of Mahabalipuram, Khajuraho, Kailashnath? Or the city of Jaipur, its havelis as well those of Samod and Shekhavati region? Let us remember that these are all based on the Vasthusastras.

Vastu-Shastra top
